How to Implement Error Monitoring in Golang

Golang, with its speed, simplicity, and concurrency features, has become a darling of backend developers. Its built-in error handling mechanisms, like the intuitive error type and the powerful recover() function, provide a solid foundation. However, as applications grow and complexity increases, relying solely on these native features can become an issue. This is where Apitoolkit, a dedicated API tool for testing platform,steps in, offering comprehensive error monitoring capabilities, monitoring error, detecting anomalies and also to elevate your Golang development.
Imagine… your application running in production, serving thousands of requests. Suddenly, an unexpected error crops up. But instead of blind scrambling, Apitoolkit’s error monitoring shines by providing:
1. Real-time error notifications: No more waiting for users to report issues. Apitoolkit instantly alerts you when errors occur, pinpointing the specific API call and providing essential context like request parameters and timestamps.
2. Detailed stack traces: Gone are the days of cryptic error messages. Apitoolkit dives deep, presenting clear and concise stack traces that guide you directly to the source of the error, saving you valuable debugging time.
3. Centralized error dashboard: Apitoolkit consolidates all your error data in a single, intuitive dashboard, allowing you to analyze trends, identify recurring issues, and prioritize fixes strategically.
4.Customizable alerting: Configure alerts based on specific error types, severities, or affected APIs. Stay informed about critical issues while suppressing low-priority noise, ensuring efficient problem solving.
But Apitoolkit’s goes beyond mere notifications. It empowers you to proactively prevent errors.
1. Automated API tests: Build and schedule comprehensive API tests to continuously check the health and functionality of your backend. Catch regressions and potential errors before they reach production, ensuring a smooth user experience.
2. Load testing: Simulate real-world usage patterns with Apitoolkit’s load testing capabilities. Identify performance bottlenecks and resource constraints before they become production headaches.
3. Mock services: Isolate external dependencies and focus on your Golang code with ease. Apitoolkit’s mock services allow you to test your application logic in a controlled environment, uncovering errors that might have been masked by external factors.
By using Apitoolkit’s error monitoring and proactive testing features, you transform your Golang backends from vulnerable codebases to resilient fortresses.
Imagine the peace of mind knowing that even when glitches inevitably appear, you’ll have a reliable toolset to identify, diagnose, and resolve them with lightning speed.
How to Handle Errors in Go Language
Go’s approach to error handling stands out for its emphasis on explicitness and value-based management. Unlike languages that rely on exceptions, Go empowers developers with direct control over error propagation and decision-making. Here’s how it works:
1. Errors as Values
Error Type: Go features a built-in error interface, defining a type that can represent any error condition.
Return Values: Functions often return multiple values, including an explicit error value to indicate success or failure.
No Exceptions: Go consciously avoids exceptions to promote clear error handling paths and avoid hidden control flow jumps.
2. Checking Errors
Explicit Checks: Developers must explicitly check for errors after function calls using
if err != nil.
Immediate Handling: This encourages immediate error handling at the point of occurrence, promoting clarity and preventing error propagation.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
)
func main() {
data, err := ioutil.ReadFile("test.txt")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Println(string(data))
}
3. Panic and Recover
Panic: When a function encounters a truly unrecoverable error, it can panic(), halting normal execution.
Recover: The recover() function can catch a panic(), allowing for logging or alternative actions.
Use Sparingly: Excessive use of panic() and recover() can make code less predictable and harder to debug.
Monitoring Golang Errors with Apitoolkit We’ve discussed Go’s error handling, but the real world throws curveballs. So how do you ensure your Go applications stay in shape during production? This is where Apitoolkit steps in, becoming your eagle-eyed guardian for pesky Golang errors.
Think of Apitoolkit as a centralized hub for all your Go application’s errors. It meticulously gathers them, sorts them out, and presents them in a way that’s both technical and approachable.
How to setup error reporting in Golang with APItoolkit
- Install the apitoolkit package: go get -u github.com/apitoolkit/apitoolkit-go
- Import the package in your Golang file: import apitoolkit “github.com/apitoolkit/apitoolkit-go”
- Create a new instance of the apitoolkit client:
ctx := context.Background()
apitoolkitClient, err := apitoolkit.NewClient(ctx, apitoolkit.Config{APIKey: "<API_KEY>"})
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
Please remember to replace <API_KEY> with your actual API key.
4.Wrap your HTTP handler function with the apitoolkit middleware:
go
helloHandler := func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
file, err := os.Open("non-existing-file.txt")
if err!= nil {
// Report the error to apitoolkit
apitoolkit.ReportError(r.Context(), err)
}
fmt.Fprintln(w, "{\"Hello\": \"World!\"}")
}
http.Handle(”/”, apitoolkitClient.Middleware(http.HandlerFunc(helloHandler)))
5. Finally, start your HTTP server:
go
if err := http.ListenAndServe(”:8089”, nil); err != nil {
fmt.Println(”Server error:”, err)
}
To check the reported errors, log in to your APItoolkit.io account and navigate to the 'Errors' section. You can filter the errors by environment, date, or error type.
Here is how APItoolkit present your errors;
Crystal-Clear Stack Traces: No more cryptic error messages. Apitoolkit dissects each error, pinpointing the exact line of code where it originated.
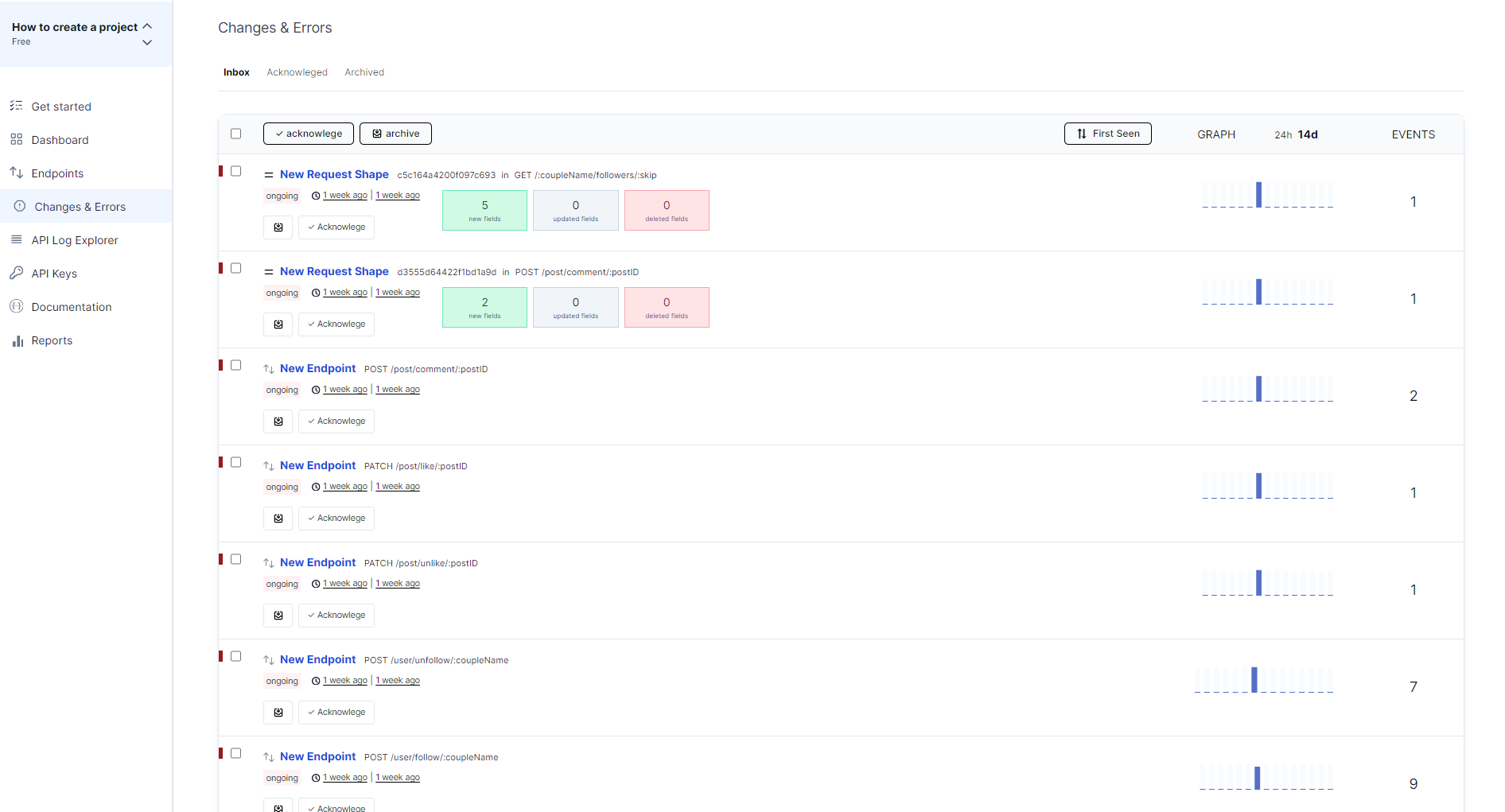
Informative Charts and Graphs: Visualize error trends over time. Identify recurring issues, track spikes in error rates, and understand how your app behaves under different loads.User Tracking: Who’s affected by which errors? Apitoolkit connects the dots, showing you which users are experiencing specific issues. Prioritize critical errors impacting large batches of users, ensuring a smooth experience for everyone.
Fequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is Apitoolkit and how does it enhance error monitoring in Golang applications?
A: Apitoolkit is a dedicated API tool for testing platforms, specifically designed to enhance error monitoring in Golang applications. It provides real-time error notifications, detailed stack traces, and a centralized error dashboard. Apitoolkit goes beyond traditional error reporting by offering features such as customizable alerting, automated API tests, load testing, and mock services to proactively prevent errors and ensure the smooth functioning of Golang backends.
Q2: How does Apitoolkit notify developers of errors in Golang applications?
A: Apitoolkit provides real-time error notifications, eliminating the need for users to report issues. When errors occur, Apitoolkit instantly alerts developers, pinpointing the specific API call and providing essential context such as request parameters and timestamps.
Q3: Can Apitoolkit help in diagnosing errors efficiently?
A: Yes, Apitoolkit aids in efficient error diagnosis by offering detailed stack traces. Instead of cryptic error messages, Apitoolkit provides clear and concise stack traces that guide developers directly to the source of the error, saving valuable debugging time.
Q4: How does Apitoolkit consolidate error data?
A: Apitoolkit consolidates all error data in a centralized and intuitive dashboard. This allows developers to analyze trends, identify recurring issues, and prioritize fixes strategically.
Q5: How does Go handle errors, and why is it different from languages using exceptions?
A: Go handles errors with an emphasis on explicitness and value-based management. It uses a built-in error interface, and functions often return multiple values, including an explicit error value to indicate success or failure. Unlike languages using exceptions, Go avoids hidden control flow jumps, promoting clear error handling paths and immediate error handling at the point of occurrence.
Conclusion
While Go’s built-in error handling offers a solid foundation, maintaining robust production-grade applications demands more. Apitoolkit bridges the gap, offering comprehensive error monitoring to keep your Go backends humming. Real-time error notifications, detailed stack traces, and customizable alerts empower you to catch and resolve issues swiftly.